How to manage risks
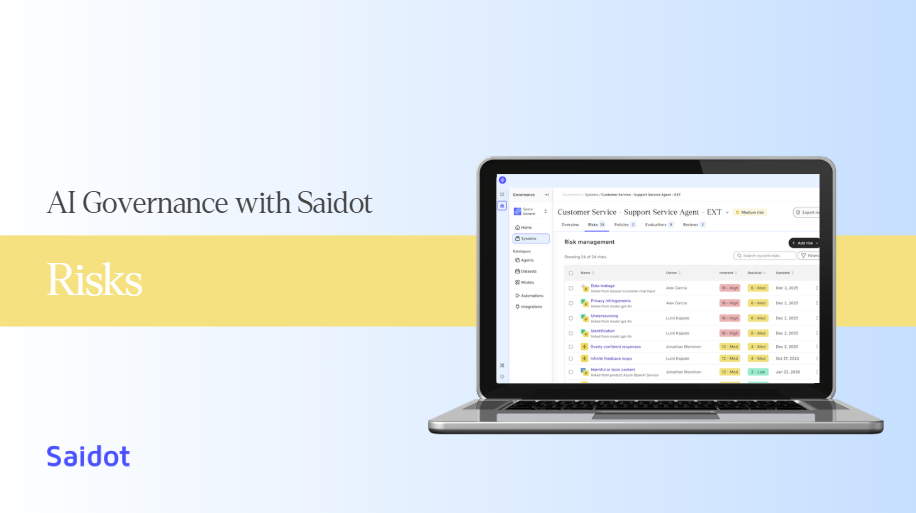
AI risk management on the Saidot platform involves identifying, evaluating, and mitigating specific risks throughout the lifecycle of the AI System. Our risk management approach and methodology follows the leading industry standards. Saidot risk management consists of the following risk management process and steps:
Identify and inherent risks
Document risks
Evaluate inherent risk level
Assign controls
Assess residual risk
Analyse and review risk posture
Step 1. Identify and inherent risks
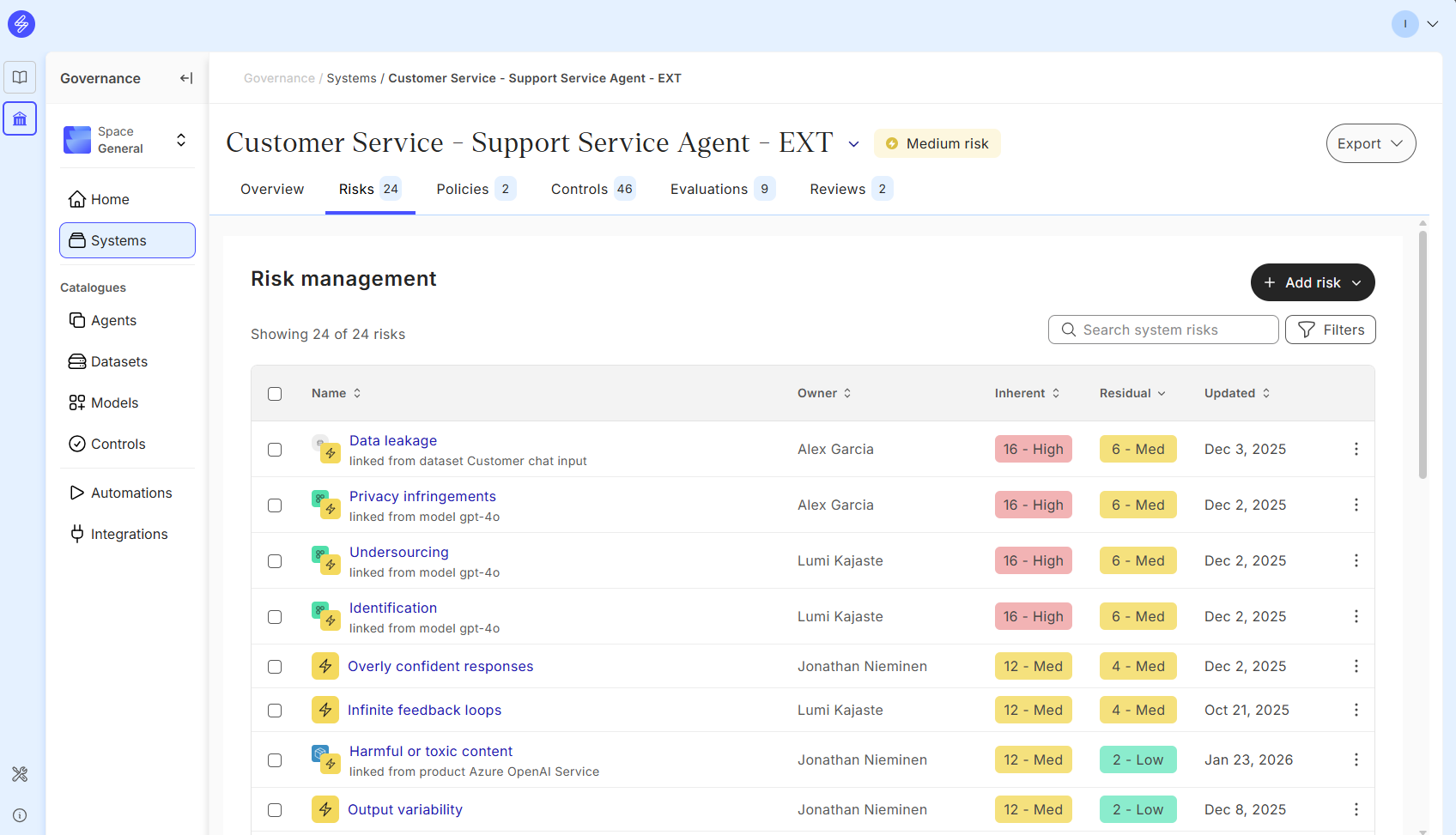
Risk management is a guided and knowledge based feature of Saidot. Our risk management methodology is based on standards and industry best practices. Start the risk management process by opening the Risks tab.
Risks can be added to systems in three ways:
Adding recommended risks from Saidot’s risk library
Recording custom risks
Inheriting risks from models, datasets and products
When using the risks in the library, the risk descriptions and mitigation suggestions are populated automatically. When recording a custom risk, the information needs to be added manually. The risk recommendations are based on the contextual information added when registering the system.
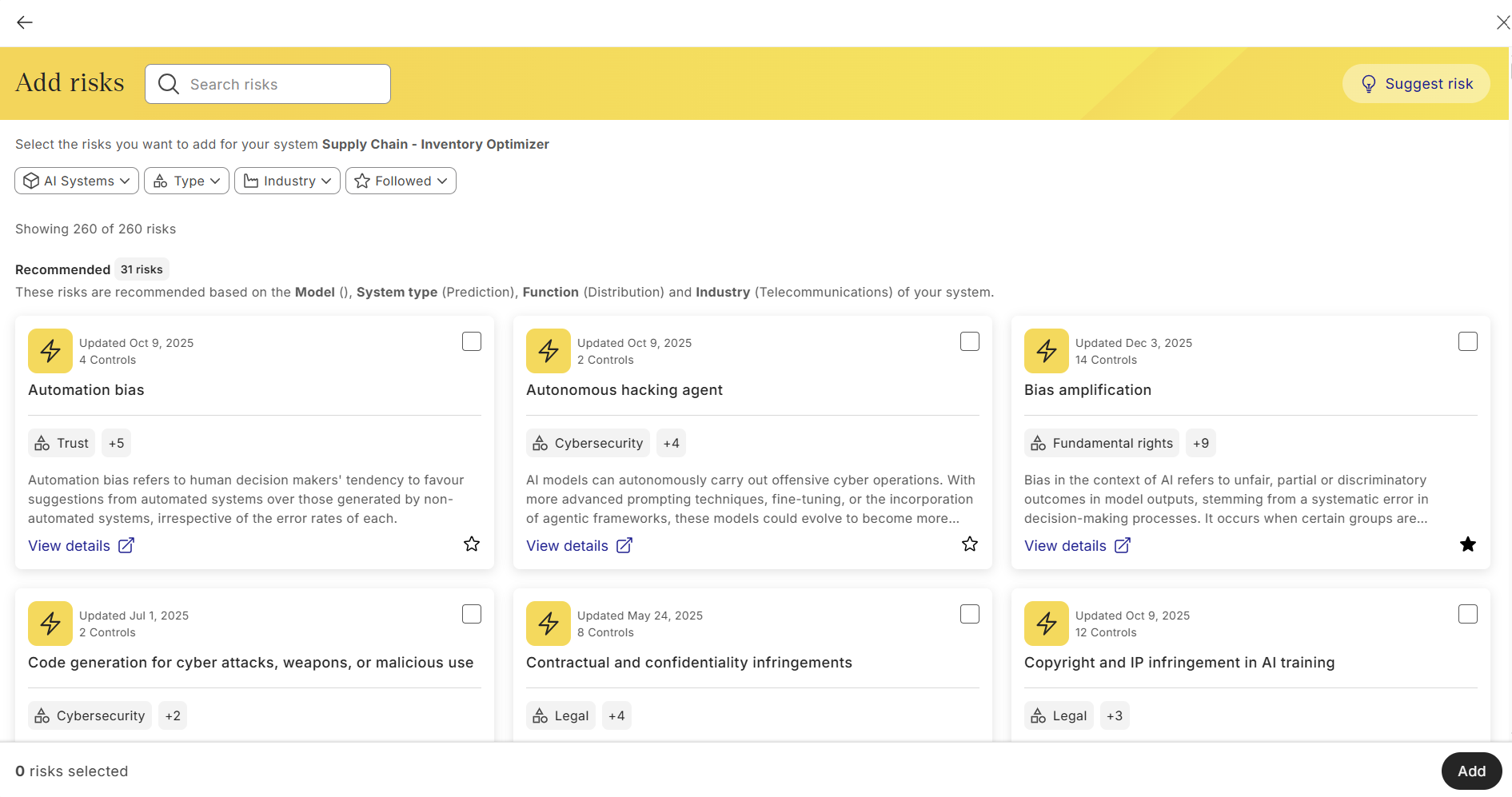
To support effective and comprehensive risk identification, Saidot platform includes an automated risk inheritance mechanism. Risk inheritance automatically surfaces risks linked to models and products, helping users identify and manage relevant risks for their AI system. In the future, risk inheritance will be extended to cover agents from the Agent Catalogue.
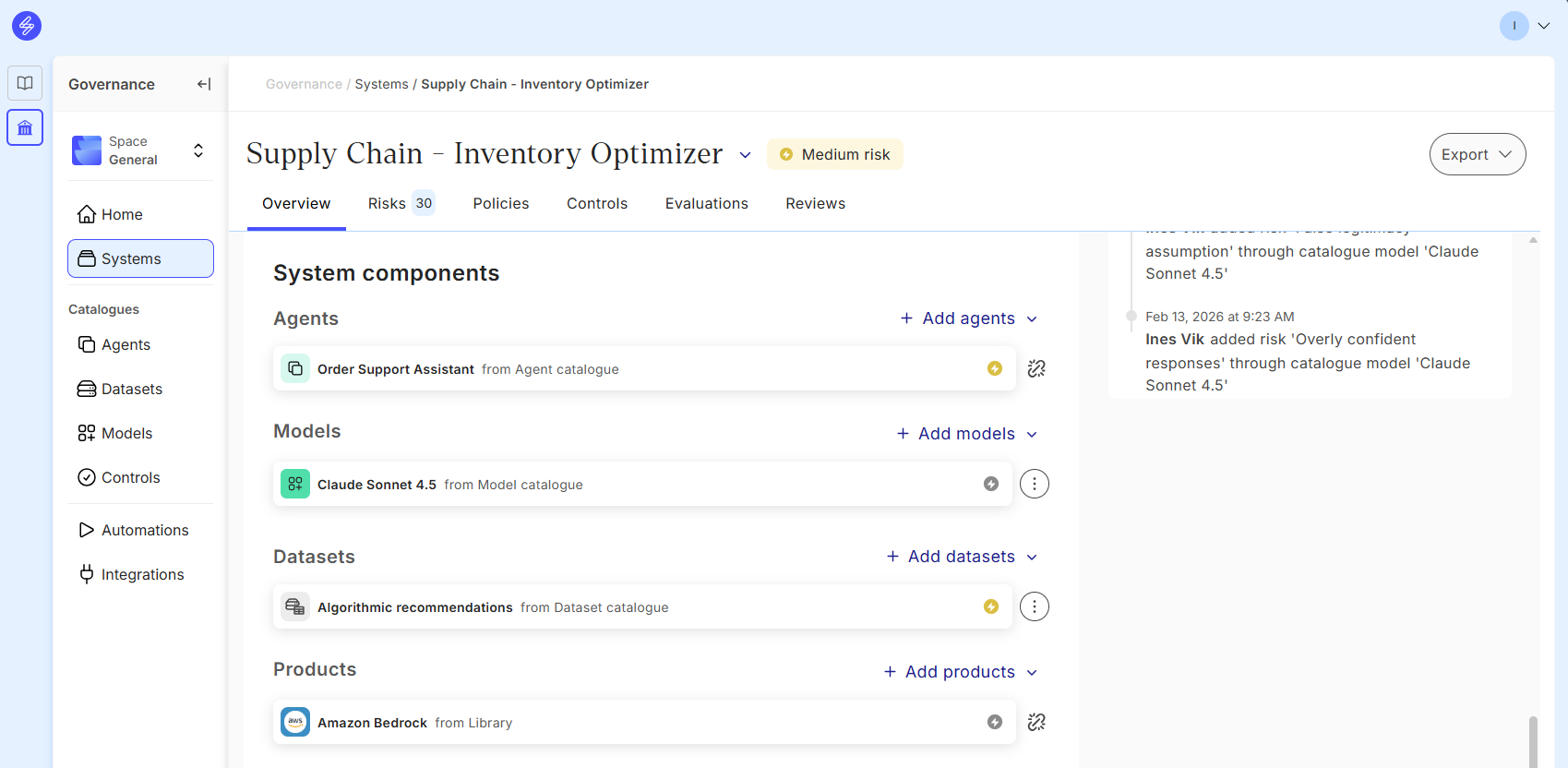
When users connect models from the catalogue or from library, or products to systems on the platform, relevant risks connected to those components are inherited. These risks are then shown in the system's risk management overview. This ensures that key risks are not overlooked and that users are proactively alerted to potential concerns based on the system's models and products.
On the platform, the following types of risks are inherited from models, products and datasets:
Model Catalogue: If a model is built on a third-party provider model, risks communicated by the provider about the model are automatically populated on the model card. Provider-identified risks are risks highlighted by a model provider in the provider's published model card pertaining to the model or in a provider's published risk framework descriptive of the specific model or model family. In addition, any model-related risks manually selected by the user, technical, legal, or otherwise, are inherited.
Model Library: Inherited risks include those communicated by the model provider.
Product Library: Inherited risks include provider-identified risks and risks arising out of Saidot’s legal and contractual analysis. Provider-identified risks are risks highlighted by a product provider in the provider's published product documentation or in a provider's published risk framework descriptive of the specific product.
Data Catalogue: The risks linked to Datasets are inherited automatically to the AI System when the linking is established directly from the Dataset Catalogue.
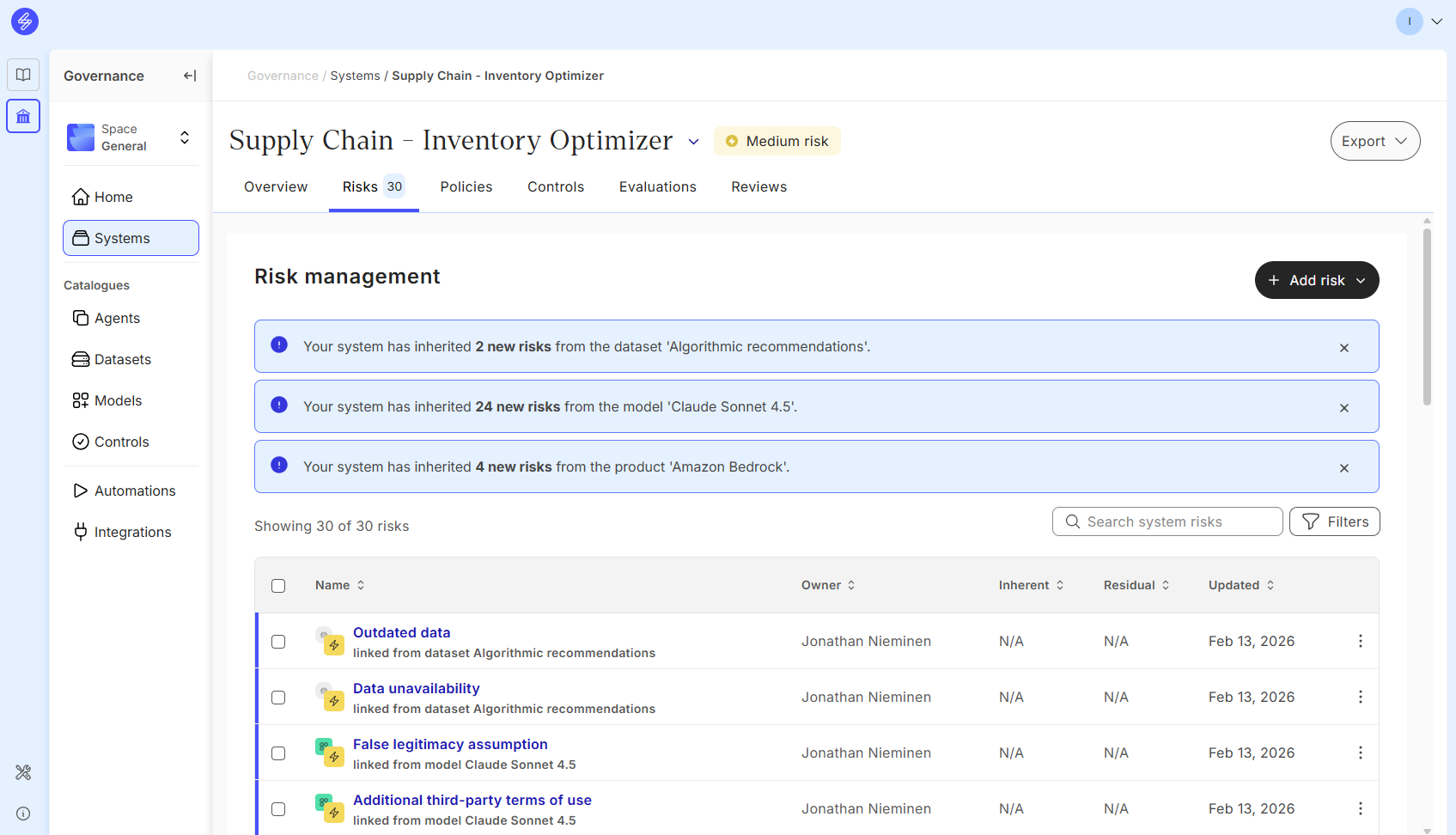
All inherited risks appear automatically in the risk management overview. If a specific risk originates from multiple sources, it will appear separately for each source to support targeted and effective mitigation strategies. Users are responsible for reviewing these risks, assessing their relevance, and prioritising them based on the specific system's context of use. Irrelevant inherited risks can be deleted from the overview if they do not apply to the use case.
Even when risks are inherited automatically, users are encouraged to review the risk recommendations to ensure comprehensive coverage. Inherited risks provide a great starting point, but they may not capture all relevant risks. We emphasise the importance of user accountability in identifying additional, context-specific risks that the platform may not surface on its own.
It is important to note that if a model or product is later removed from a system, and the risks are removed at the same time, any risks that were inherited from it will no longer appear in the risk management tab. This removal requires user confirmation to ensure essential risks are not unintentionally deleted. Once confirmed, the inherited risks and any corresponding data are deleted from risk management.
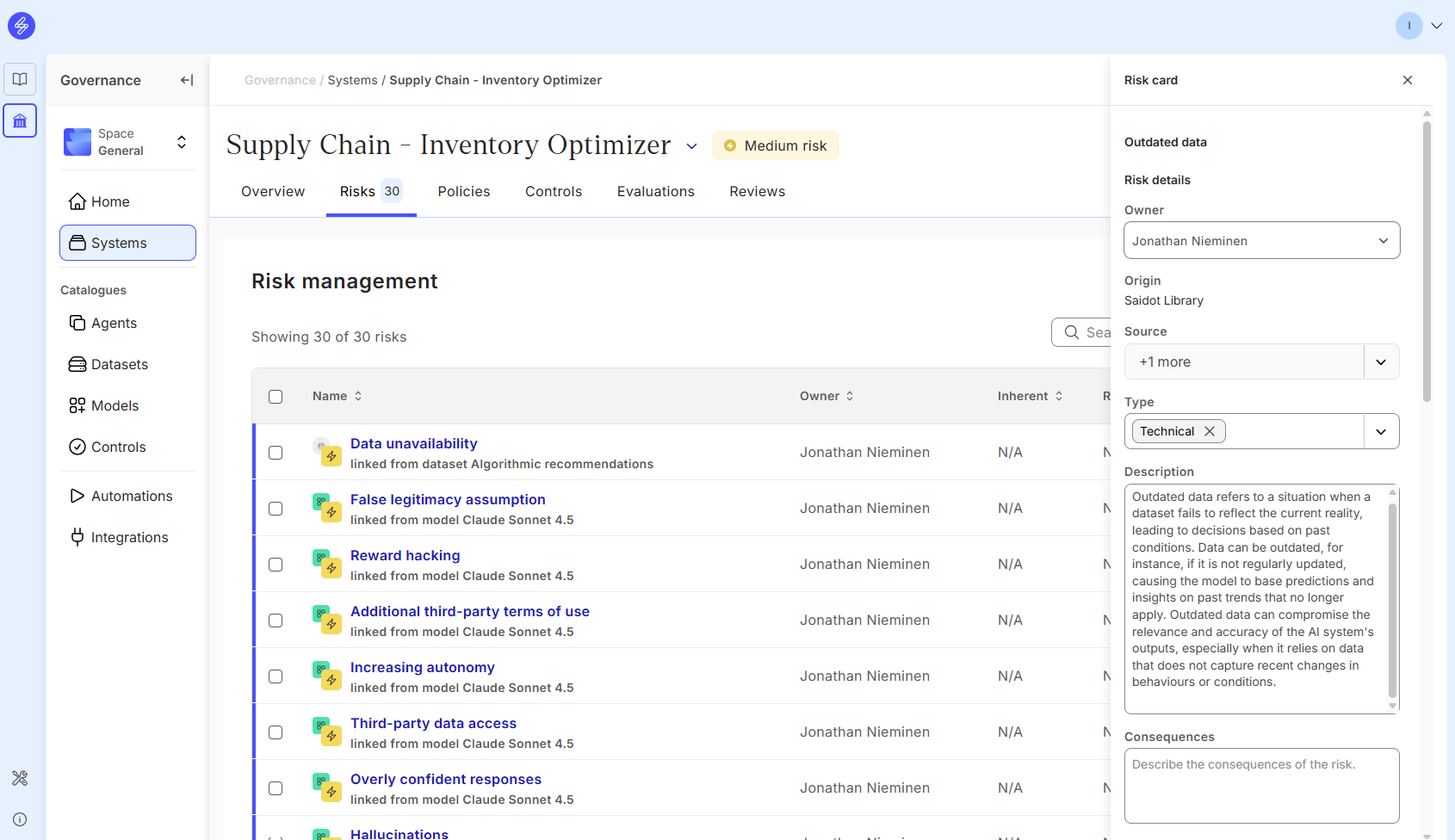
Step 2. Document risks
Risk documentation includes the risk owner, risk source, risk type and risk description. When using a risk from the Saidot risk library, the risk description is populated automatically but they can be edited if needed. Contextual risk consequences can be described separately.
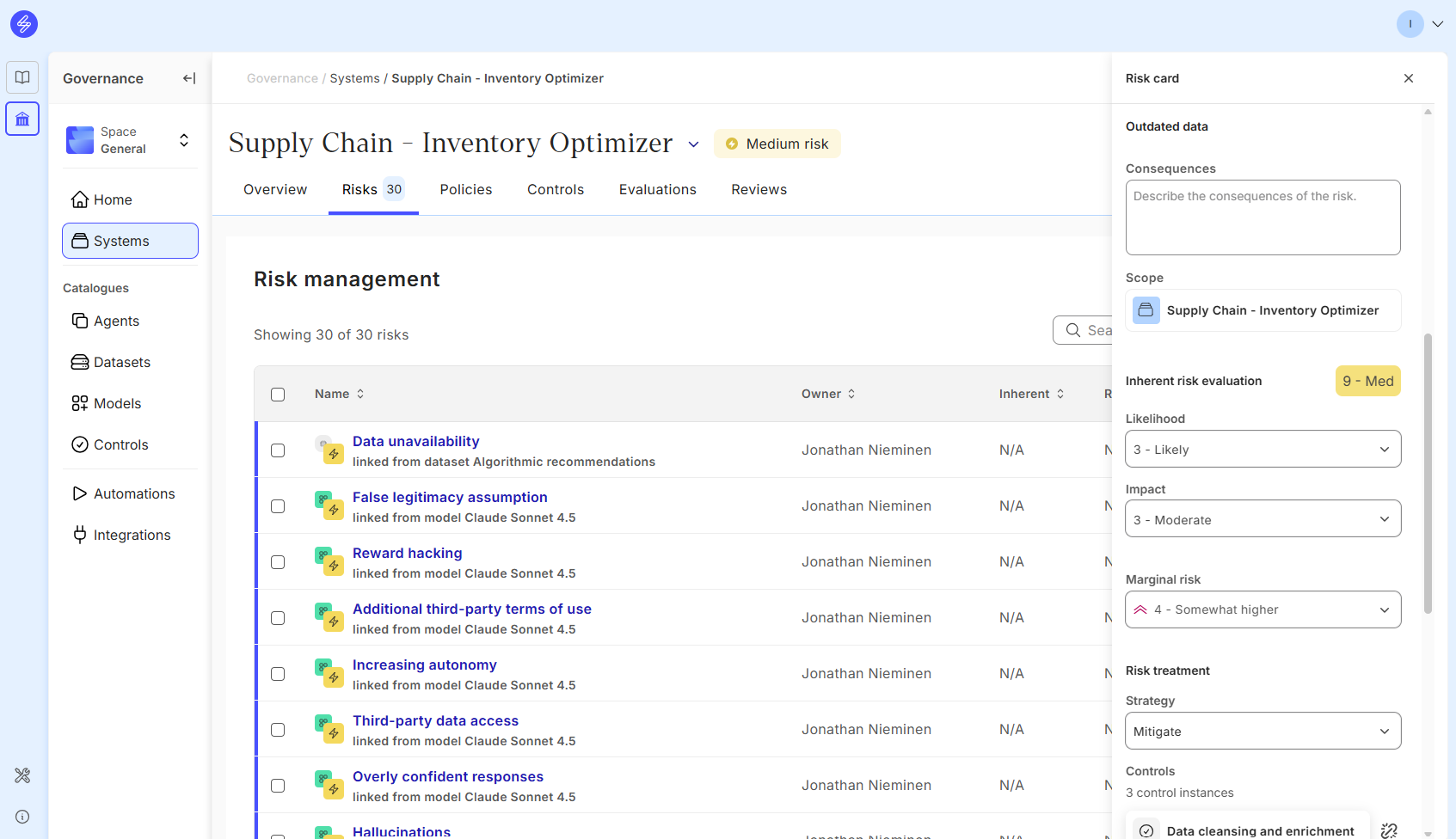
Step 3. Evaluate risks
Analyse the inherent risk level, indicating the risk level before controls have been implemented. In Saidot, risk level is defined based on likelihood and impact in four levels.
Likelihood:
1 - Rare: The likelihood of the risk scenario is very low
2 - Unlikely: The likelihood of the risk scenario is low
3 - Likely: The likelihood of the risk scenario is significant
4 - Very likely: The likelihood of the risk scenario is high
5 - Almost certain: The likelihood of the risk scenario is very high
Impact:
1 - Negligible: Minimal impact on the organisation's operations, affected individuals or society
2 - Minor: Degradation in the performance of the organisation with no consequences for affected individuals or broader society
3 - Moderate: Noticeably reduces the organisation's operational efficiency. Possible significant consequences for affected individuals or broader society
4 - Major: Adversely affects the organisation's capacity to operate. Likely irreversible damage to organisations, affected individuals or broader society
5 - Severe: Consequences extend beyond the organisation. Serious implications for organisations, individuals or broader society
.png?inst-v=b1f00b4d-d6a8-4a87-8d9d-81a83b4fb8e5)
Analyse also marginal risk level describing the change in risk that occurs as a result of the introduction of AI technology.
1 - Significantly smaller: Significantly reduced risk level due to the introduction of AI
2 - Somewhat smaller: Somewhat reduced risk level due to the introduction of AI
3 - Same: Similar risk level due to the introduction of AI
4 - Somewhat higher: Somewhat higher risk level due to the introduction of AI
5 - Significantly higher: Significantly higher risk level due to the introduction of AI
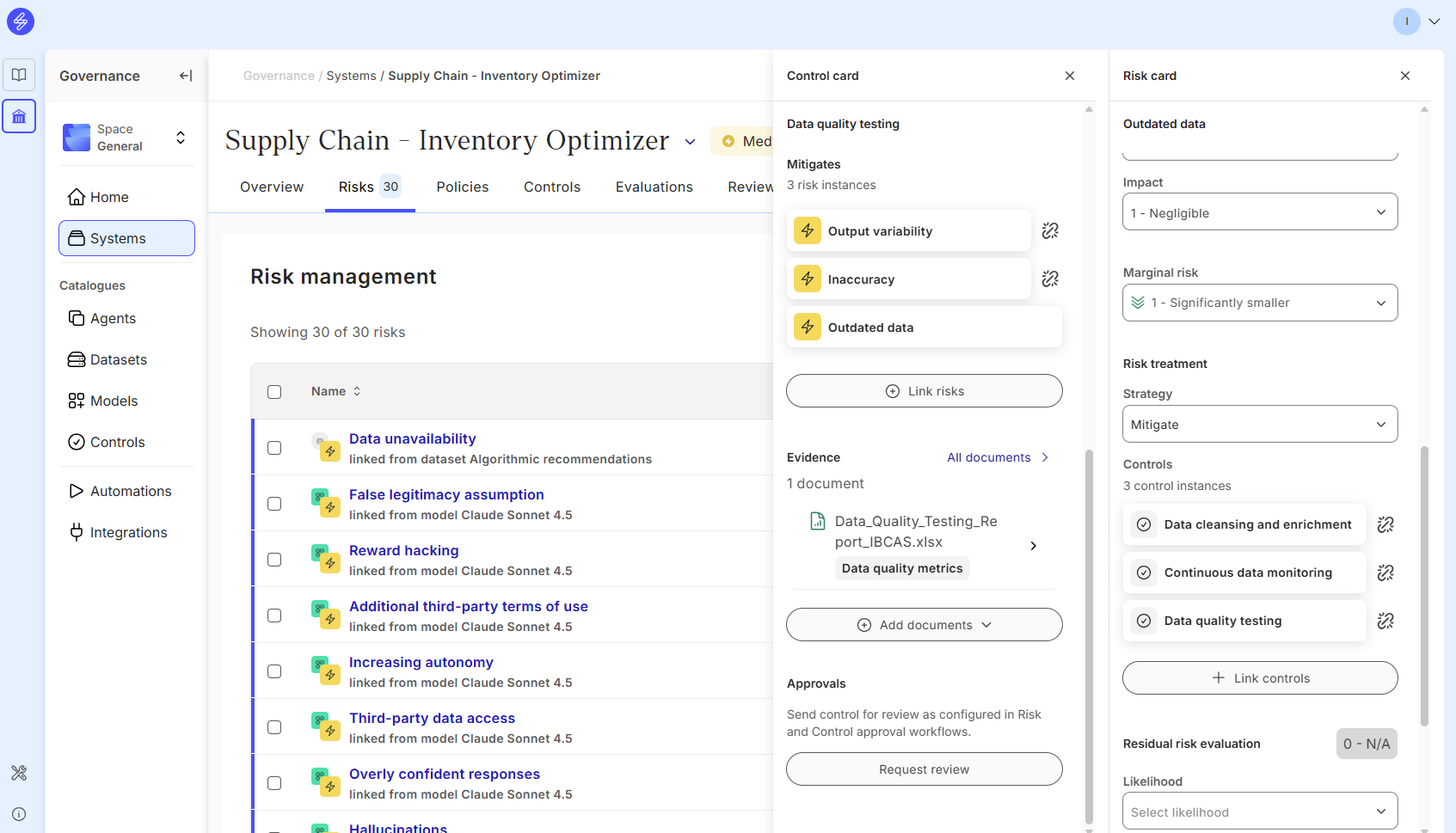
Step 4. Link risk controls
Select a risk treatment strategy according to the inherent risk level and our recommendations. The treatment strategy selection should be aligned with company’s risk appetite and right size governance approach. Typically,
Risk level is green: Accept
Risk level is yellow or red: Mitigate or Avoid
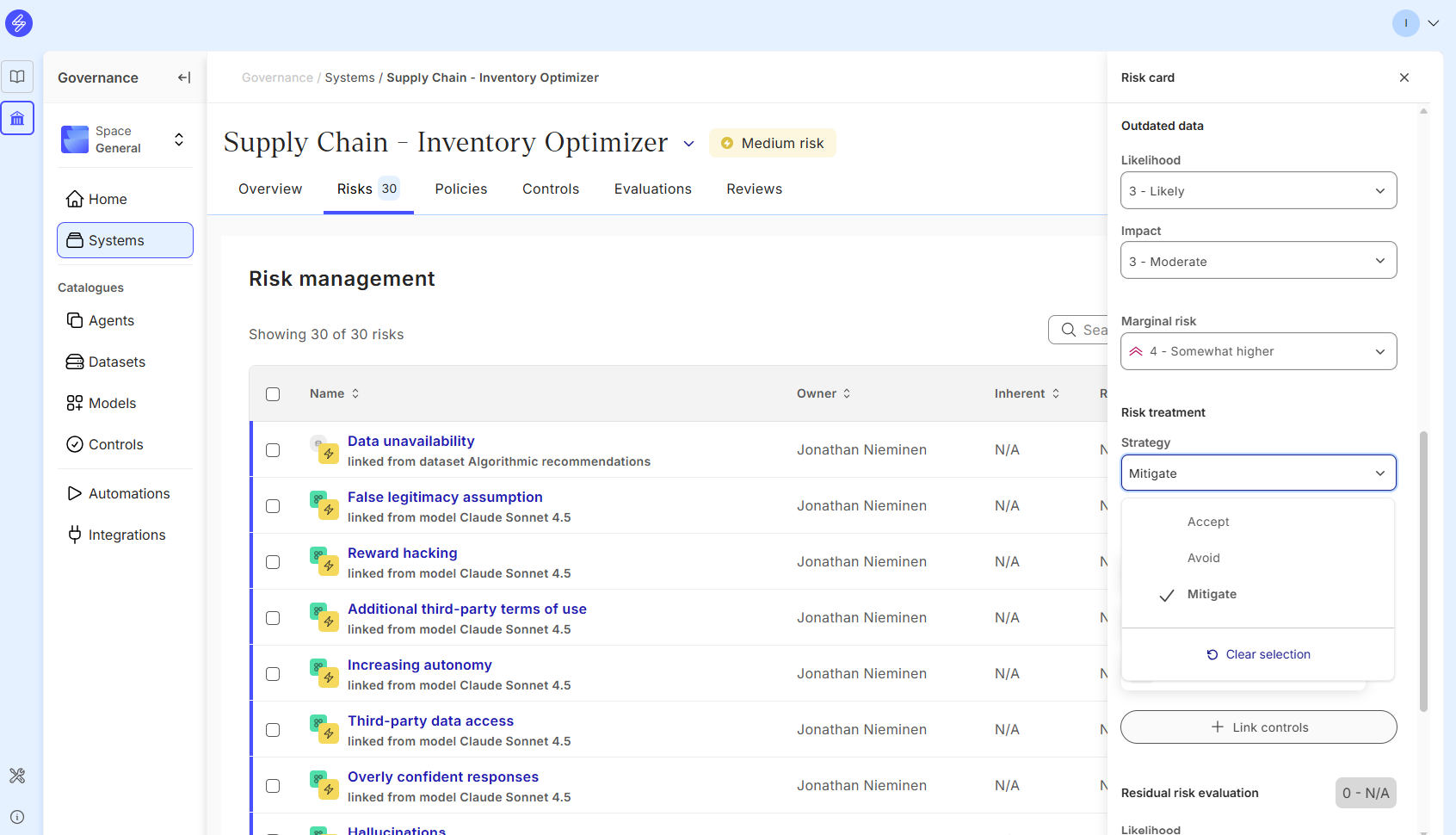
If you are using a Risk from the Saidot risk library, you can import controls suitable for risk treatments. You may also add your own custom controls.
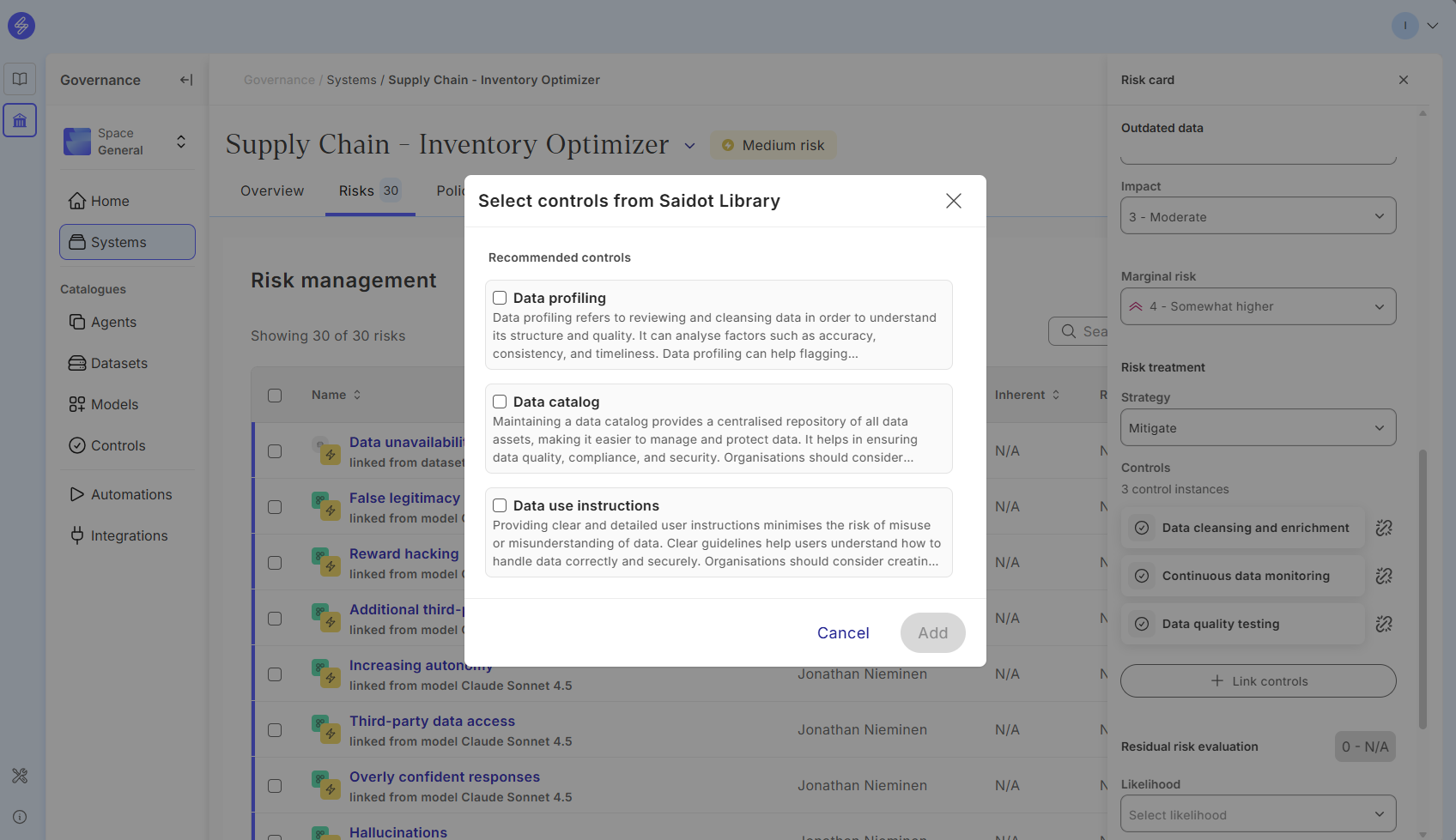
In the control panel you can edit the control Lifecycle stage, due date, status and description.
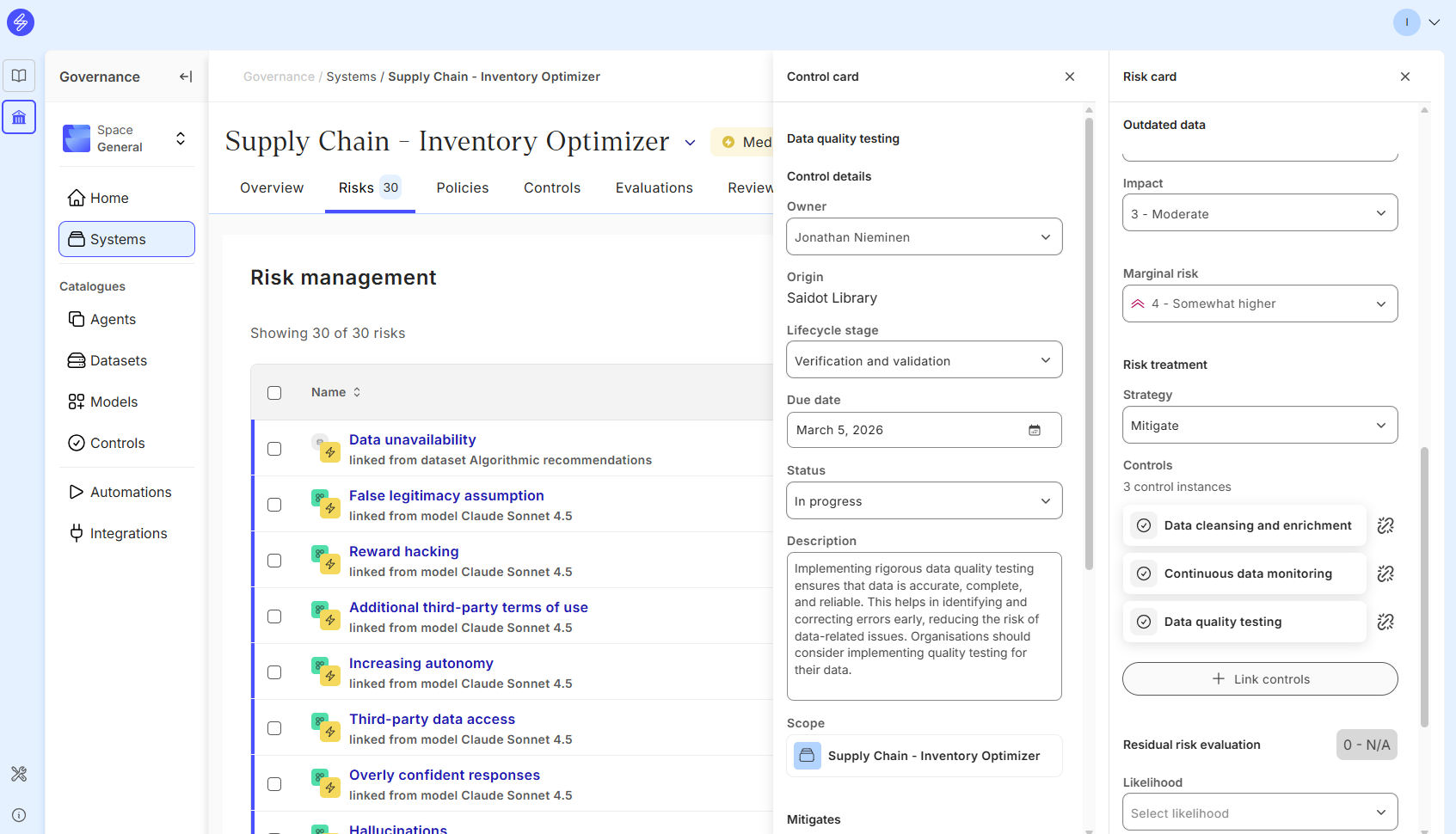
You can also link the control to another risk, add evidence or delete the control.
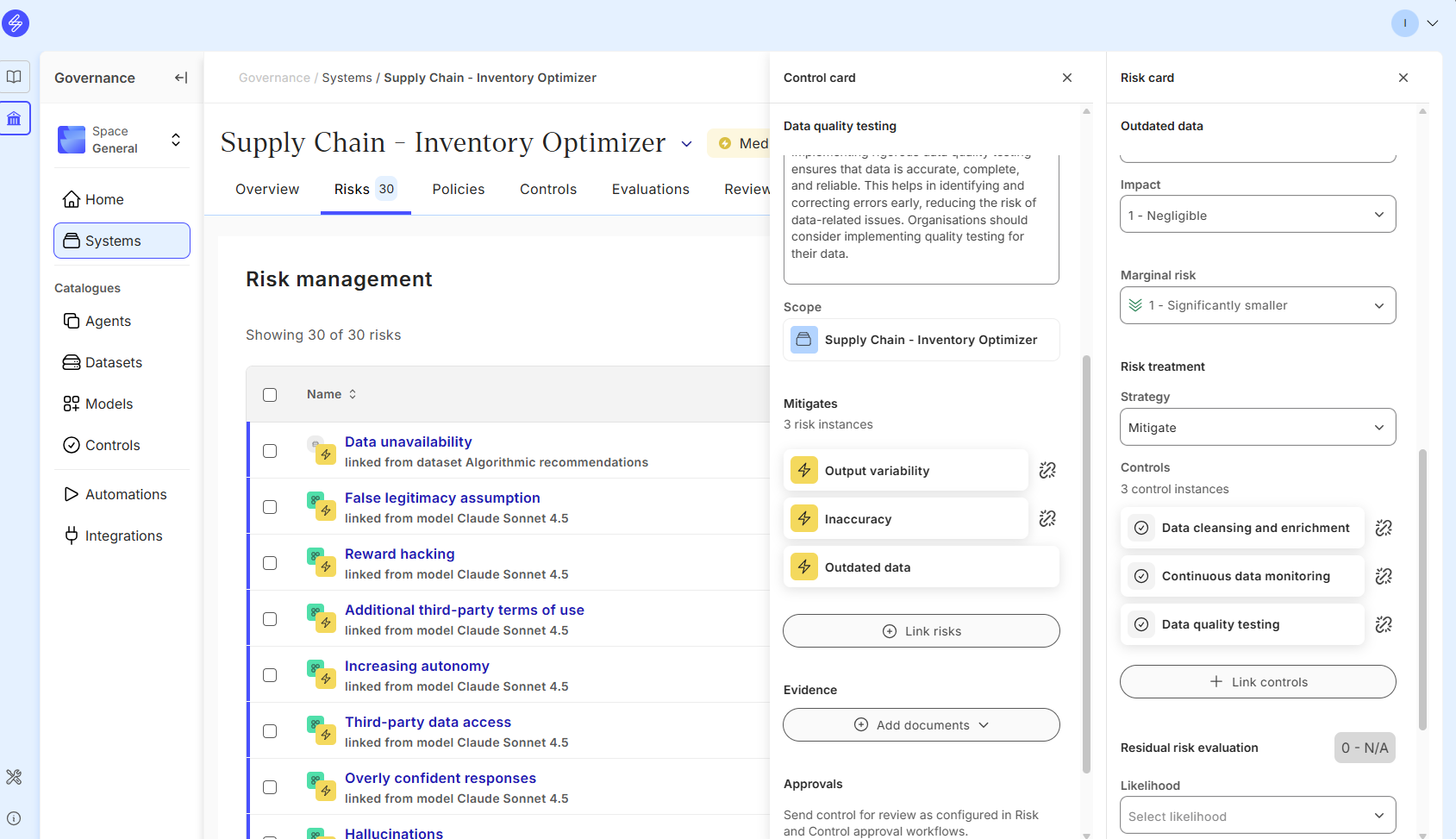
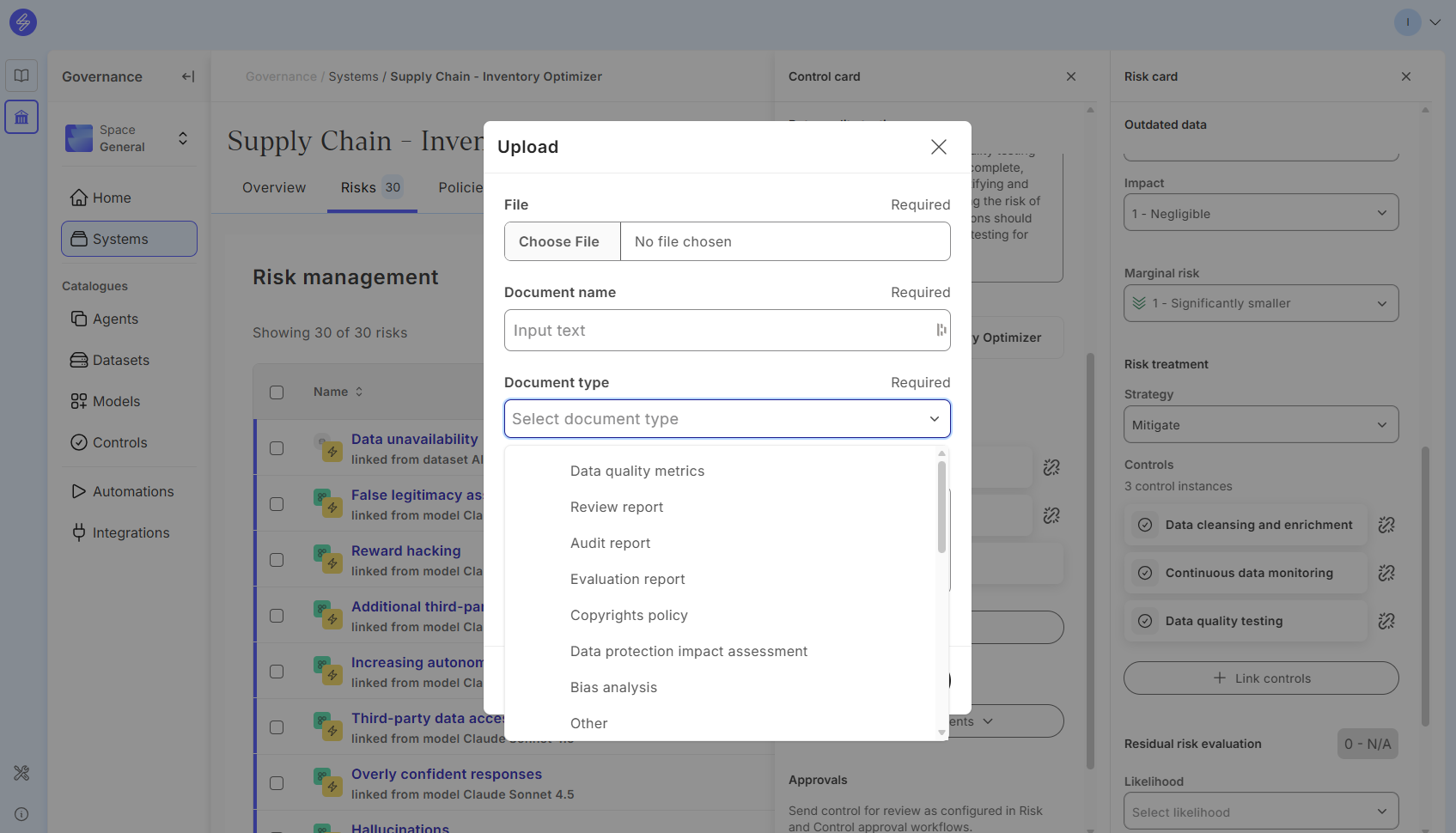
The control card allows you to add documents as evidence. Evidence can be added by uploading a document or adding a link to the document.
The Saidot admins and Space managers can configure automated workflow that enables Control specific review and approval. If the workflow is configured, the approval request button appears below Evidence documentation.
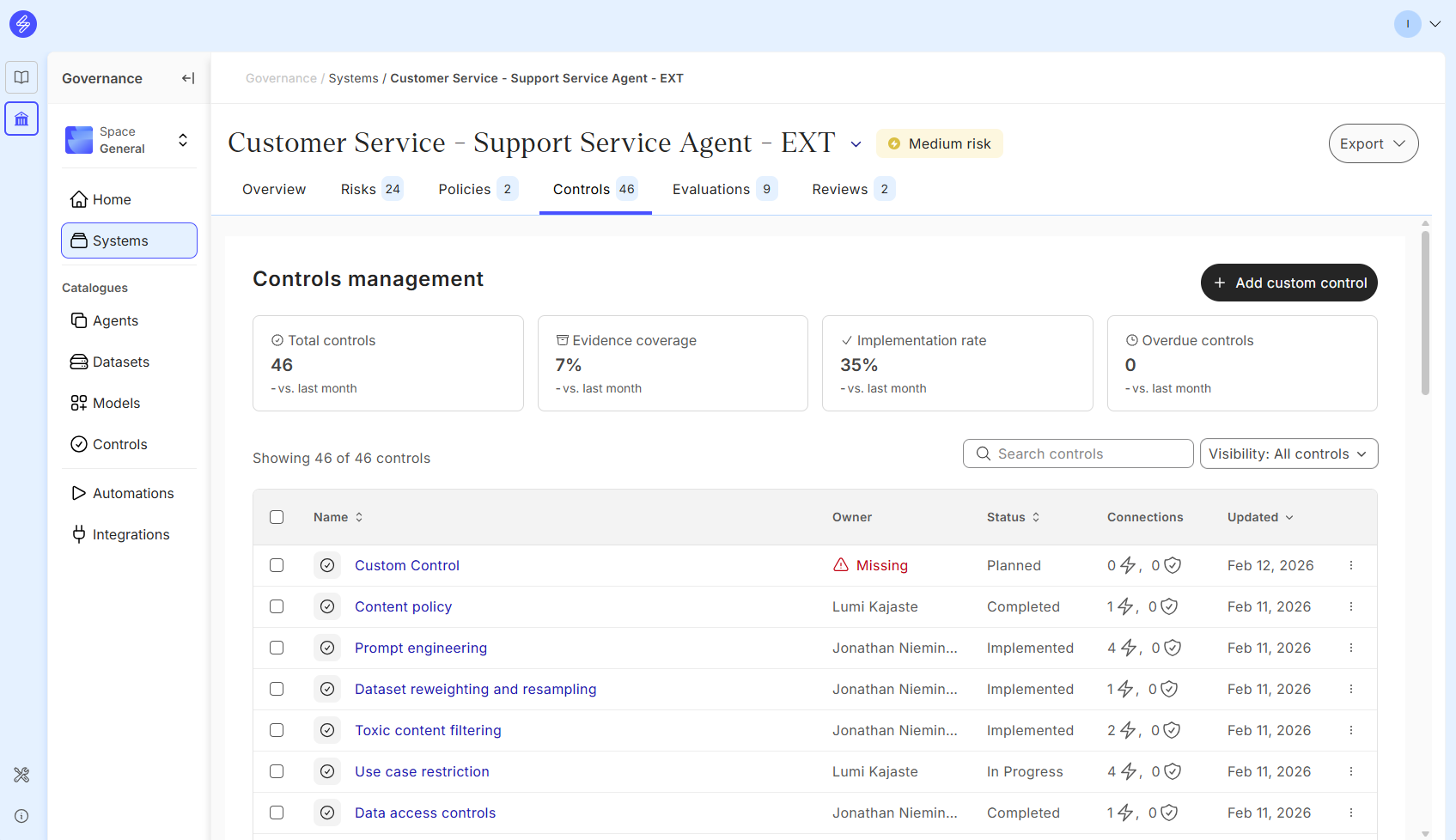
Step 5. Manage risk controls
Risk controls can also ten assessed and managed in the Controls tab. Control-tab allows users to analyse overall control implementation and evidence coverage status.
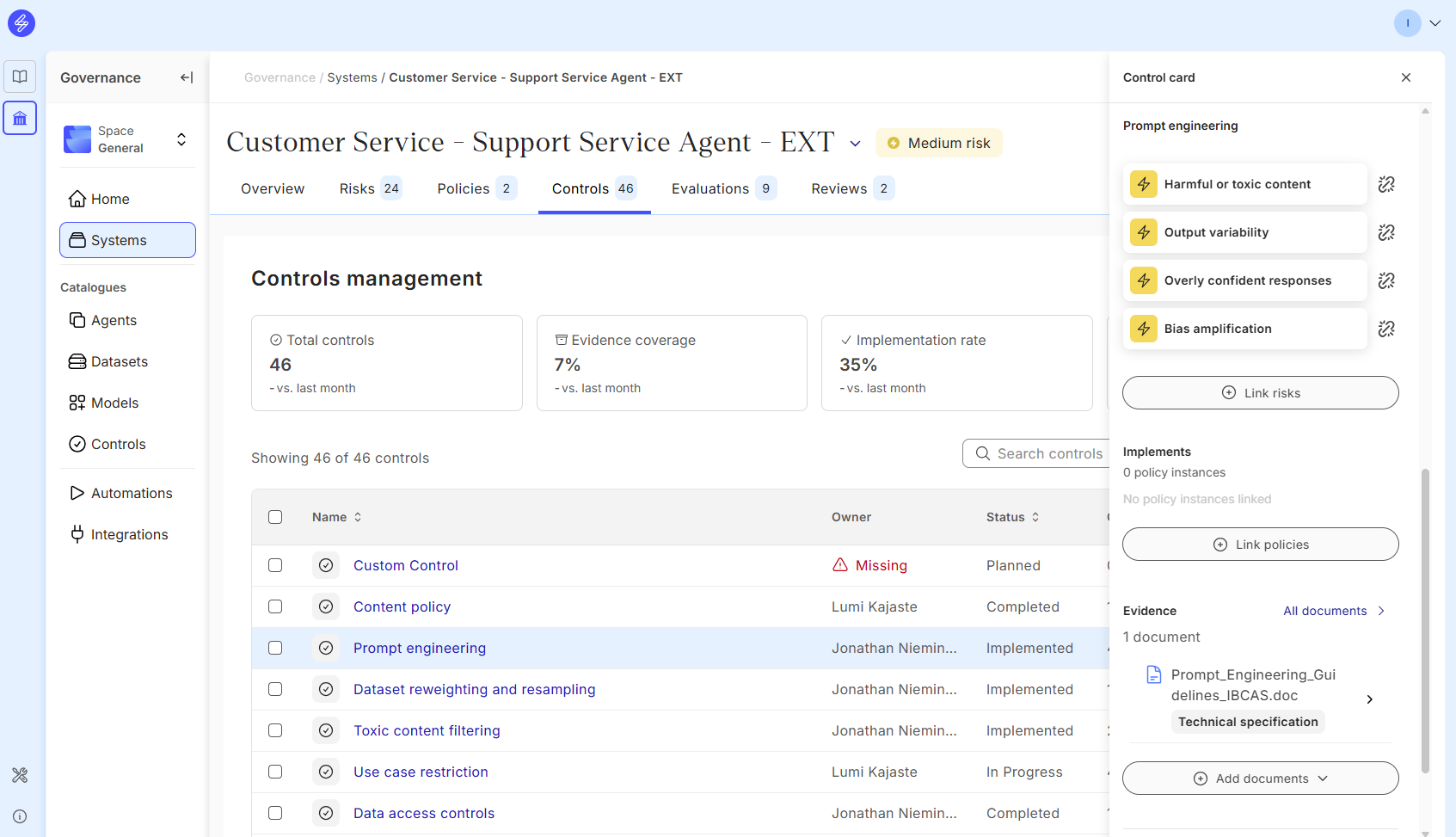
Control cards can be used in this tap in a similar way as in Risks tab:
Manage the status and ownership of the controls
Cross link controls to other risks
Add evidence
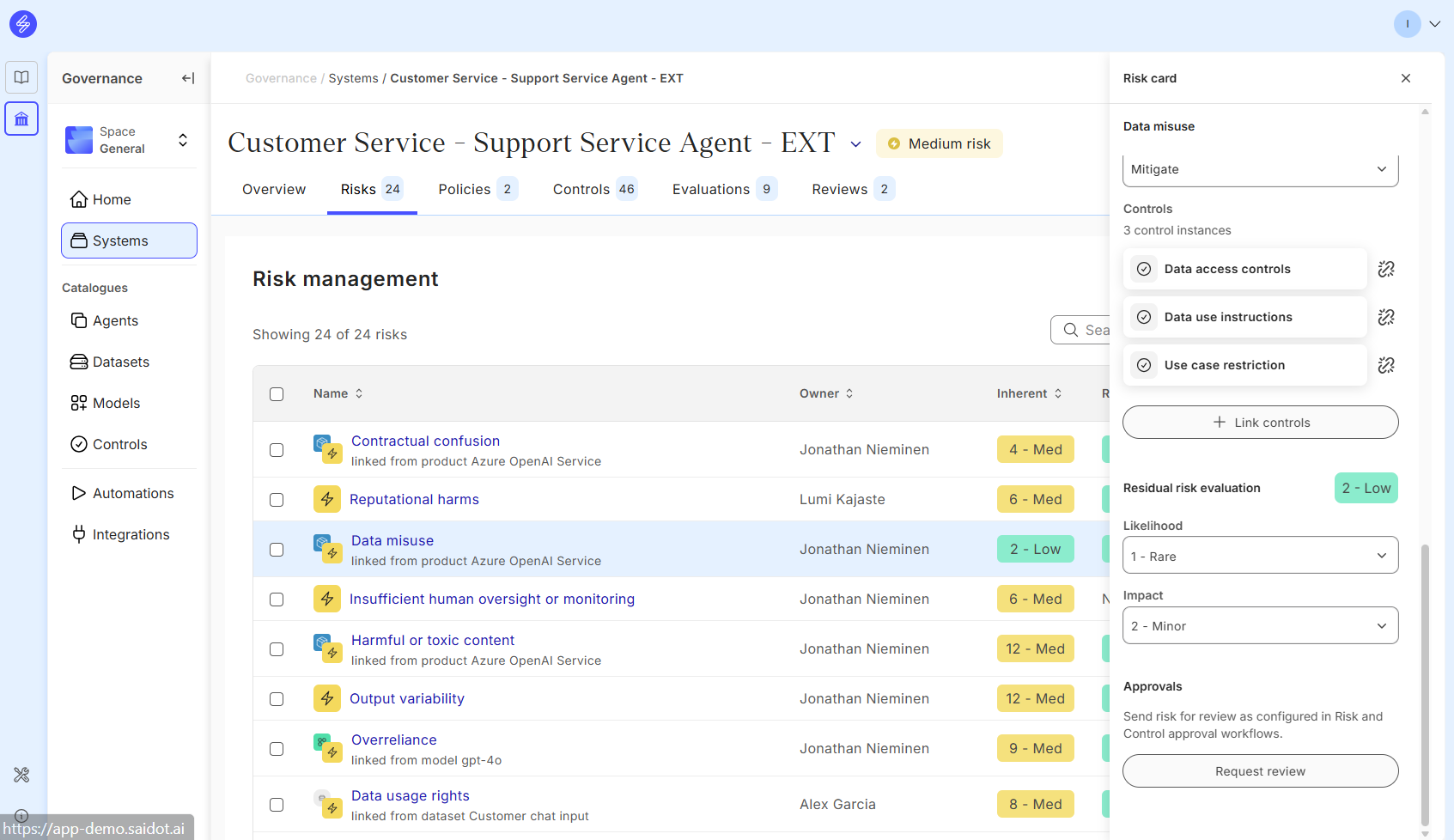
Step 6. Assess residual risk
After selecting and implementing the treatments, select the treatment status and assess the residual risk. Residual risk describes the risk level after the treatments have been implemented.
Step 6. Analyse and review risk posture
The main Risk tab view offers visibility to Risks, where they are inherited, their owner, inherent and residual risk levels and whenthe risk has been recently updated.
The transparency report can be used to analyse risk posture, mitigation status based on residual risk levels.
